Testicular cancer facts
Rates of testicular cancer
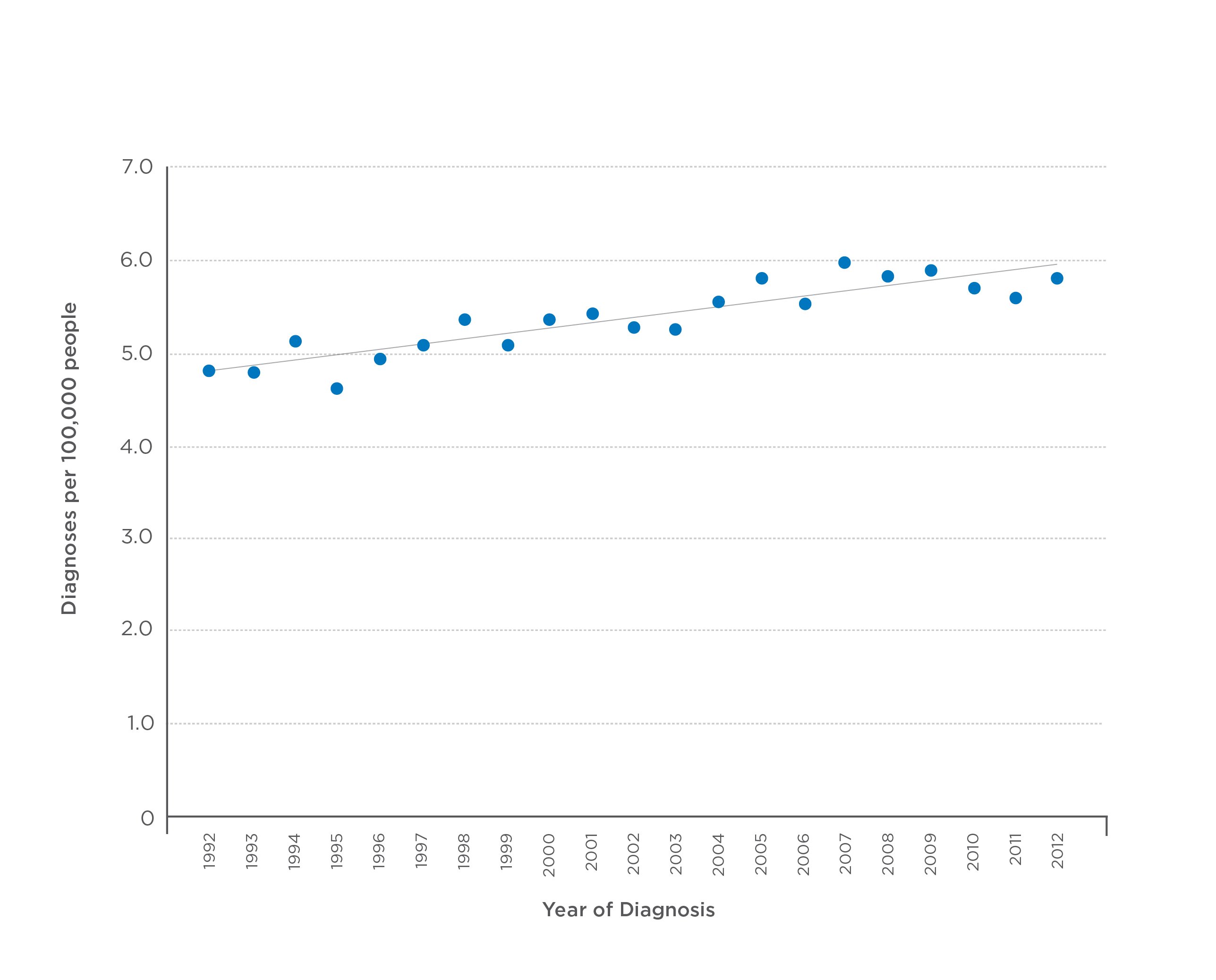 Rates for U.S. population. Data from the National Cancer Institute Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results Program. Source: seer.cancer.gov
Rates for U.S. population. Data from the National Cancer Institute Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results Program. Source: seer.cancer.govTesticular cancer is relatively uncommon, but there have been small increases in diagnoses in recent years.
Good news: Survival rates are excellent, with more than 95 percent of patients surviving for five years. However, treatment – including surgery, radiation and chemotherapy – can result in impairment and morbidity.
Risk of this form of cancer is greatest in men between 20 and 40 years old.
Risk factors: Exposures and events that happen in utero and early life are thought to be the most important, including:
- Family history of testicular cancer.
- Exposure to pesticides; the chemical perfluorooctanoic acid, or PFOA, the chemical used in Teflon; and other chemicals such as benzene and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, or PAHs, chemicals related to combustion and petroleum products.
- Being born with an undescended testicle.
- Taller men are also at greater risk, likely due to the underlying biology of sex and growth hormones that control puberty and growth rate, which are related to height.
Prevention tips:
- Avoid and seek alternatives to pesticides. Mulch, landscape fabrics, manual weeding, and homemade solutions of salt and vinegar or soap can help kill weeds. Control insects at home by not leaving food out, cleaning up crumbs, keeping a space around your home’s foundation free of vegetation and debris, and using a dehumidifier for moisture control.
- EWG’s Dirty DozenTM list can help you identify and avoid produce with the highest levels of pesticide residues.
- Don’t use worn or scratched nonstick cookware, and avoid stain-resistant treatments on carpets and upholstery.
- Avoid exposures to benzene, PAHs and toxic byproducts of combustion by:
- Not smoking.
- Keeping indoor air clean, including by using a vacuum with a HEPA filter.
- Using a water filter.
- Using the air recirculating option in your car when in heavy traffic.
- Wearing proper protective equipment when working with exposures to heavy smoke or toxic chemicals.
Use EWG’s Skin Deep® and Healthy Cleaning guides to avoid other potentially toxic exposures.
Perform self-exams – any suspicious lumps or soreness in the testicles should be examined by a doctor.